Hypertension Medication Comparison Tool
Personalized Medication Comparison
Answer a few questions about your health profile to see which hypertension medication might be best for you based on efficacy, side effects, cost, and your specific conditions.
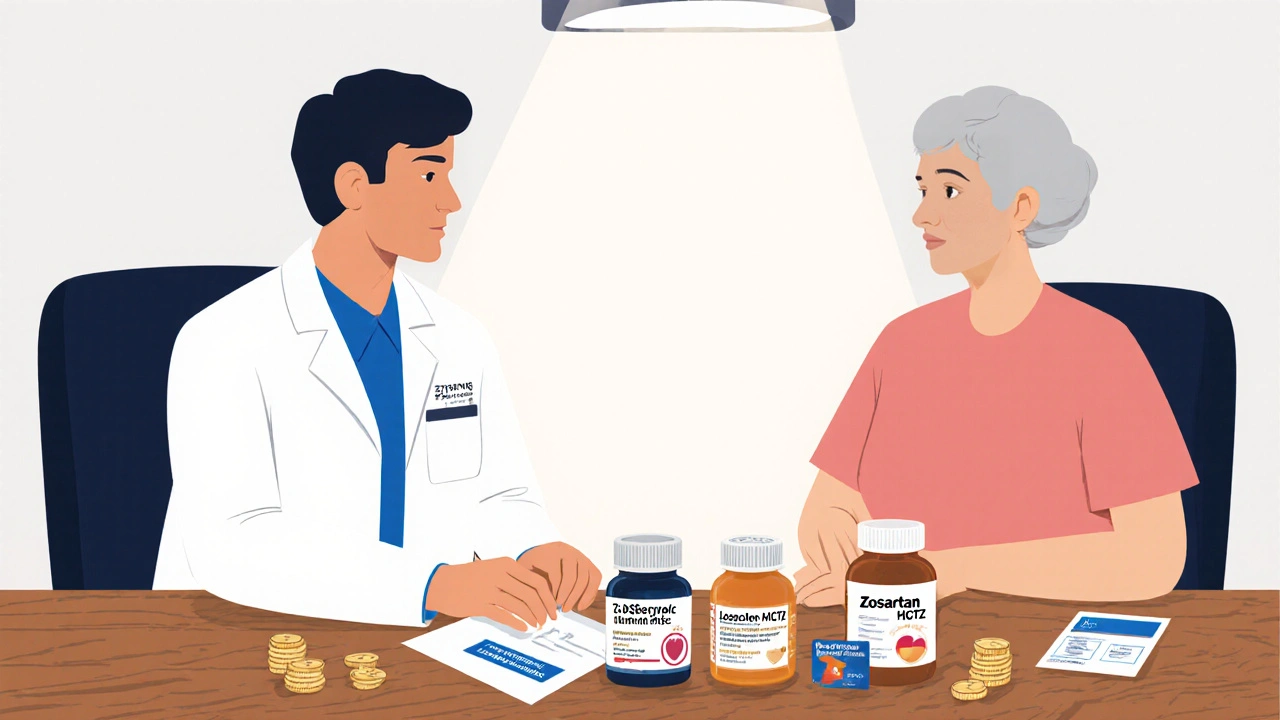
High blood pressure affects nearly half of adults in the U.S., and many are prescribed a single pill that packs two drugs together. Zestoretic alternatives are a hot topic because patients want to know if that combo is the best fit or if another option might work better for their lifestyle and health profile.
Key Takeaways
- Zestoretic combines an ACE inhibitor (lisinopril) with a thiazide diuretic (hydrochlorothiazide) to lower blood pressure from two angles.
- Common alternatives include other ACE‑inhibitor combos, ARB‑diuretic combos, and single‑agent therapies.
- When choosing, consider efficacy, side‑effect profile, kidney function, cost, and whether a generic version is available.
- Patients with a history of cough, low potassium, or certain drug interactions may benefit from an ARB‑based combo instead.
- Insurance coverage and out‑of‑pocket cost often tip the scale between Zestoretic and its competitors.
What Is Zestoretic?
Zestoretic is a prescription tablet that merges lisinopril, an ACE inhibitor, with hydrochlorothiazide, a thiazide diuretic. Approved by the FDA in 1999, the combo targets two key mechanisms: it relaxes blood vessels and helps the kidneys flush excess sodium, which together lower systolic and diastolic pressure.
How the Two Components Work
Lisinopril is an angiotensin‑converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor. By blocking the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, it prevents the powerful vasoconstrictor from tightening the arteries. The result is smoother blood flow and reduced workload for the heart.
Hydrochlorothiazide works in the distal convoluted tubule of the kidney, encouraging the excretion of sodium and water. Less fluid means lower blood volume, which eases pressure on vessel walls.
When paired, these agents often achieve blood‑pressure goals faster than either drug alone, and patients avoid taking two separate pills.
Who Might Benefit From Zestoretic?
- Adults with stage1 or stage2 hypertension who need more than one mechanism to control pressure.
- Patients without a history of ACE‑inhibitor cough or angio‑edema.
- Individuals whose potassium levels are normal; thiazides can lower potassium, so monitoring is essential.
- Those looking for a convenient once‑daily regimen.
Popular Alternatives
Below are the most frequently considered substitutes. Each offers a slightly different balance of efficacy, side effects, and cost.
- Losartan/Hydrochlorothiazide - an ARB combined with the same diuretic. ARBs tend to cause less cough.
- Enalapril/Hydrochlorothiazide - another ACE‑inhibitor combo, but Enalapril often requires twice‑daily dosing.
- Chlorthalidone - a thiazide‑like diuretic with a longer half‑life, sometimes used alone or with an ACE inhibitor.
- Exforge (amlodipine + valsartan) - a calcium‑channel blocker paired with an ARB, useful for patients with peripheral edema.
- Single‑agent ACE inhibitors such as lisinopril alone, for people who tolerate the drug but don’t need diuretic support.
Side‑Effect Snapshot
All antihypertensives carry risks. Understanding common complaints helps you weigh trade‑offs.
| Drug | Typical Side Effects | Serious Risks |
|---|---|---|
| Zestoretic | Cough, dizziness, increased urination | Angio‑edema, severe electrolyte imbalance |
| Losartan/HCTZ | Headache, fatigue, mild potassium loss | Hyperkalemia (if combined with potassium‑sparing agents), renal impairment |
| Enalapril/HCTZ | Dry mouth, light‑headedness, increased urination | Angio‑edema, worsening kidney function |
| Chlorthalidone (solo) | Muscle cramps, nocturia, mild dizziness | Severe hyponatremia, gout flares |
| Exforge | Swelling of ankles, flushing, dizziness | Hypotension, severe liver enzyme elevation (rare) |
Cost and Insurance Landscape (2025)
Pricing changes yearly, but the following ranges give a realistic picture for a 30‑day supply.
- Zestoretic (brand) - $45‑$55; generic lisinopril/hydrochlorothiazide - $8‑$12.
- Losartan/HCTZ - generic $10‑$15; brand (Hyzaar) $60‑$70.
- Enalapril/HCTZ - generic $12‑$18.
- Chlorthalidone - generic $4‑$6 (single drug).
- Exforge - brand $80‑$95; generic versions expected 2026.
If your plan prefers generics, the lisinopril/hydrochlorothiazide combo often wins on price. However, some insurers categorize Zestoretic as a “preferred brand,” leading to lower copays for patients on that specific product.

Decision Guide: When to Choose Zestoretic
- Efficacy first: If you need a strong blood‑pressure drop within weeks, the ACE‑inhibitor plus diuretic combo has proven rapid results.
- Convenience matters: One pill a day simplifies adherence, especially for older adults.
- Kidney health: Check your eGFR. ACE inhibitors protect kidneys in diabetics, but they can worsen function if baseline renal impairment is severe.
- Side‑effect tolerance: If you’ve developed a dry cough on lisinopril before, an ARB‑based combo (e.g., Losartan/HCTZ) is a smoother alternative.
- Cost sensitivity: If out‑of‑pocket cost is the biggest hurdle, the generic version of the combo or a single‑agent ACE inhibitor plus a cheap thiazide (like chlorthalidone) may be cheaper.
Monitoring and Follow‑Up
Regardless of the drug you pick, regular check‑ins are crucial. Aim for these labs at baseline and after three months:
- Serum electrolytes (especially potassium and sodium).
- Creatinine and eGFR to gauge kidney impact.
- Blood pressure readings at least twice a week until stable.
If you notice persistent cough, swelling, or sudden dizziness, contact your clinician-those signs often flag the need to switch.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I take Zestoretic with other blood‑pressure meds?
Yes, doctors sometimes add a calcium‑channel blocker or a beta‑blocker for resistant hypertension, but they will watch for overlapping side effects like low potassium or excessive blood‑pressure drops.
What should I do if I develop a dry cough on Zestoretic?
A cough is a classic ACE‑inhibitor reaction. Your doctor may switch you to an ARB‑based combo such as Losartan/HCTZ, which usually eliminates the cough.
Is the generic version of Zestoretic as effective as the brand?
Generic lisinopril‑hydrochlorothiazide contains the same active ingredients and is bioequivalent, so effectiveness is comparable. Some patients notice a slight taste difference, but clinical outcomes remain the same.
How long does it take for Zestoretic to lower blood pressure?
Most people see a measurable drop within 2‑4 weeks, with the full effect appearing by 6‑8 weeks. Consistent daily dosing and lifestyle changes speed the process.
Can Zestoretic be used during pregnancy?
No. ACE inhibitors and thiazide diuretics are classified as pregnancy‑category D. They can harm the developing fetus, so doctors switch pregnant patients to safer options like methyldopa.
Bottom Line
Choosing the right hypertension medication is a balance of how well it lowers pressure, how tolerable it is, and what your wallet can handle. Zestoretic offers strong, convenient control for many, but alternatives such as Losartan/HCTZ or a simple thiazide‑like chlorthalidone can be smarter picks when cough, kidney concerns, or cost dominate the conversation. Talk with your clinician, review your lab results, and consider how each option fits your daily routine.





Lila Tyas
October 12, 2025 AT 22:13Hey folks! If you’re juggling blood pressure meds, this tool is a solid starting point. It quickly points out where Zestoretic shines and where alternatives might fit better. Don’t forget to factor in how you feel day‑to‑day, not just the numbers. A little dose of curiosity can go a long way toward better control. Keep the conversation going and share what works for you!
Mark Szwarc
October 14, 2025 AT 02:00From a pharmacologic perspective, Zestoretic combines an ACE inhibitor with a thiazide, giving it strong BP‑lowering potency. The ACE component, however, carries the classic dry‑cough risk, which can be a deal‑breaker for some patients. Losartan/HCTZ swaps the ACE for an ARB, eliminating cough but sometimes offering slightly less renal protection, especially in diabetic cohorts. Exforge uses a calcium‑channel blocker plus ARB, excellent for peripheral edema but often comes at a premium price. When you weigh efficacy against side‑effects and cost, the optimal choice really hinges on individual tolerance and financial constraints. Remember to discuss any switch with your provider to avoid abrupt BP spikes. Also, monitor potassium levels if you’re on a thiazide, as hypokalemia can creep in unnoticed.
BLAKE LUND
October 15, 2025 AT 05:46Zestoretic waltzes in, coughs out, and leaves you breathless-literally.
Veronica Rodriguez
October 16, 2025 AT 09:33Great breakdown, Mark! 😊 Adding to that, the cost gap between generic Zestoretic and its brand counterpart can be quite noticeable, especially for long‑term therapy. Also, many insurers favor generic combos, which can shave off $5‑$10 per month. Keep an eye on formulary tiers if you’re on a high‑deductible plan. Lastly, a quick labs check after any switch will catch electrolyte shifts early.
Holly Hayes
October 17, 2025 AT 13:20Honestly, who even reads these tool‑tips? It’s like trying to choose a Netflix show while you’re already bored out of your mind. Zestoretic might be “fast‑acting,” but have you considered the melodrama of a dry cough that just won’t quit? And let’s not even get started on the generic‑brand price tango-$8‑$12 versus $45‑$55 feels like a scam. If you’re into saving pennies, just stick with the cheap version and hope for the best. At the end of the day, it’s all just a pricey guess, right?
Matthew Shapiro
October 18, 2025 AT 17:06Looking at the numbers, Zestoretic’s generic cost sits around $8‑$12 per month, which is pretty reasonable. The Losartan/HCTZ combo is slightly pricier at $10‑$15, but still affordable for most plans. Exforge’s brand price, however, jumps to $80‑$95, making it the least budget‑friendly option. If cost is a primary concern, the ACE‑diuretic combo often gives the best bang for your buck. Always check your pharmacy’s price‑matching policies; sometimes you can snag a better deal.
Julia Phillips
October 19, 2025 AT 20:53When I first read about Zestoretic, I imagined a sleek, high‑tech gadget that could magically tame my stubborn hypertension. Instead, it turned out to be a modest pill, yet its impact felt like a crescendo in a quiet symphony. The absence of a cough was a sigh of relief-a subtle, almost poetic return to normal breathing. Meanwhile, the alternative combos each brought their own flavor: Losartan/HCTZ whispered calm, while Exforge shouted with bold calcium‑channel vigor. It’s fascinating how a tiny tablet can stir such drama in our bodies, a reminder that medicine is as much art as science. In the end, the choice is personal, shaped by our own narratives and tolerances. I hope this tool helps you script a healthier chapter.
Richa Punyani
October 21, 2025 AT 00:40Dear colleague, I extend my sincere appreciation for the eloquent reflections shared. It is imperative, however, to weigh the clinical data alongside the narrative sentiment. While Zestoretic may indeed provide symptomatic relief, one must also consider renal function parameters in the long term. Moreover, cost considerations cannot be dismissed in a formal health‑economic assessment. Should you elect to transition, a structured titration protocol is advisable. Please ensure baseline laboratory evaluations are documented prior to any pharmacologic alteration. I remain at your disposal for further discourse on this matter.
Bhupendra Darji
October 22, 2025 AT 04:26Hey everyone, just wanted to chime in that I’ve tried both Zestoretic and Losartan/HCTZ. In my experience, the ACE combo knocked my BP down faster, but the cough was a nuisance. The ARB combo felt gentler on the lungs, though it took a bit longer to see results. If you’re okay with a little cough, Zestoretic’s speed is worth it; otherwise, the ARB route is a solid fallback. Happy to share more details if anyone’s interested.
Robert Keter
October 23, 2025 AT 08:13Allow me to expand upon the considerations already laid out, for the benefit of those seeking a more granular understanding of the pharmacodynamic intricacies involved in antihypertensive combination therapy. Firstly, the synergistic effect of an ACE inhibitor paired with a thiazide diuretic, as exemplified by Zestoretic, results not only in vasodilation but also in a reduction of plasma volume, thereby achieving a dual mechanism that can be especially advantageous in patients with volume‑dependent hypertension. Secondly, the propensity for ACE inhibitors to increase bradykinin levels, while clinically beneficial in certain contexts, also predisposes to the well‑documented adverse event of a dry, persistent cough; this side effect arises from elevated levels of substance P and neuropeptides that sensitize the cough reflex. Thirdly, the alternative ARB‑based combination, Losartan/HCTZ, circumvents this bradykinin pathway, thus mitigating cough risk, but it may also offer slightly less renoprotective efficacy, particularly in patients with diabetic nephropathy, due to differences in angiotensin‑II receptor blockade specificity. Fourth, Exforge, which couples an ARB with a calcium‑channel blocker, introduces an additional hemodynamic effect via inhibition of L‑type calcium channels, leading to arterial smooth muscle relaxation and an attenuation of peripheral vascular resistance; however, this comes at the expense of higher direct costs and a distinct side‑effect profile that includes peripheral edema, a consequence of preferential venodilation. Fifth, from an economic perspective, the generic formulation of Zestoretic, priced between eight and twelve dollars per month, presents a compelling cost‑effectiveness ratio when juxtaposed against the brand‑only pricing of Exforge, which can ascend to ninety‑five dollars, thereby imposing a significant financial burden on patients without comprehensive insurance coverage. Sixth, it is essential to monitor serum electrolytes, particularly potassium, as thiazide diuretics can precipitate hypokalemia, a condition that may exacerbate arrhythmic risk if left unchecked; concomitant use of potassium‑sparring agents should be considered where appropriate. Seventh, the impact on renal function should be routinely evaluated via eGFR measurements, especially in individuals with baseline impairment, given that both ACE inhibitors and ARBs can initially cause a modest rise in serum creatinine, reflecting hemodynamic changes within the glomerulus. Eighth, patient adherence is often influenced by dosing convenience; once‑daily regimens, such as those offered by these combination pills, have been shown to improve compliance relative to multiple‑pill strategies. Ninth, clinicians must remain vigilant regarding drug‑drug interactions, particularly with NSAIDs, which can attenuate the antihypertensive efficacy of both ACE inhibitors and ARBs and increase the risk of acute kidney injury. Tenth, the selection of therapy should be individualized, taking into account comorbid conditions such as heart failure, where ACE inhibitors have proven mortality benefits, versus scenarios where ARBs might be preferentially employed due to intolerance. Eleventh, lifestyle modifications, including dietary sodium restriction and regular physical activity, remain cornerstone interventions that potentiate pharmacologic treatment effects. Twelfth, the pharmacokinetic profiles of these agents, including half‑life and metabolic pathways, should be matched to patient routines to minimize peak‑trough variability. Thirteenth, the role of patient education cannot be overstated; individuals should be informed about potential signs of electrolyte disturbance, edema, or persistent cough that warrant timely medical review. Fourteenth, in the context of polypharmacy, deprescribing unnecessary agents can reduce pill burden and improve overall therapeutic outcomes. Finally, integrating shared decision‑making, where clinicians and patients collaboratively weigh efficacy, side‑effect profiles, and cost considerations, ultimately leads to a more satisfactory and sustainable hypertension management plan.
Rory Martin
October 24, 2025 AT 12:00It is worth noting that pharmaceutical conglomerates often conceal the true financial motives behind the promotion of certain drug combinations. One should remain skeptical of the proclaimed superiority of brand‑name medications, especially when generic alternatives exist. Independent monitoring of blood pressure outcomes is essential.
Maddie Wagner
October 25, 2025 AT 15:46We appreciate your caution, Rory, and agree that critical evaluation is vital. While remaining vigilant, it’s also important to recognize that many patients genuinely benefit from evidence‑based therapies. Open dialogue with healthcare professionals can help navigate the complexities without resorting to fear. Let’s continue supporting each other in making informed choices.